The efficiency and performance of electrical machines depend on several key factors, one of the most important being the winding factor. This crucial parameter plays a significant role in optimizing the electromagnetic performance of motors, generators, and transformers. In this guide, we will explore what winding factor is, why it matters, and how it impacts the efficiency of electrical machines.
What is Winding Factor?
The winding factor, also known as the coil pitch factor, is a parameter that determines how effectively the windings of an electrical machine generate a magnetic field. It is a measure of how well the coils in the stator or rotor are arranged to maximize the machine’s efficiency.
Mathematically, the winding factor (KW) is defined as:
Where:
- K_D = Distribution factor (accounts for how the coils are distributed around the stator slots)
- K_P = Pitch factor (measures the effect of coil shortening on voltage generation)
A higher winding factor indicates better efficiency in electrical energy conversion, reducing energy losses and improving machine performance.
Why is Winding Factor Important?
Understanding and optimizing the winding factor is crucial for several reasons:
- Maximizing Efficiency – Electrical machines with an optimized winding factor operate more efficiently by reducing energy losses.
- Minimizing Harmonics – A well-designed winding pattern helps reduce unwanted harmonic distortion, which can impact machine performance and lifespan.
- Enhancing Power Output – By improving the utilization of the magnetic field, the machine can produce more power with the same input energy.
- Reducing Copper Losses – A better winding arrangement ensures lower resistance and reduces heat generation, leading to improved durability and performance.
Factors Affecting Winding Factor
Several design parameters influence the winding factor in an electrical machine:
1. Coil Pitch
The coil pitch refers to the distance between two active coil sides. Ideally, a full-pitch winding (360° electrical degrees) results in the highest winding factor, but it is not always practical. Reducing the coil pitch helps to minimize harmonics but slightly reduces the fundamental winding factor.
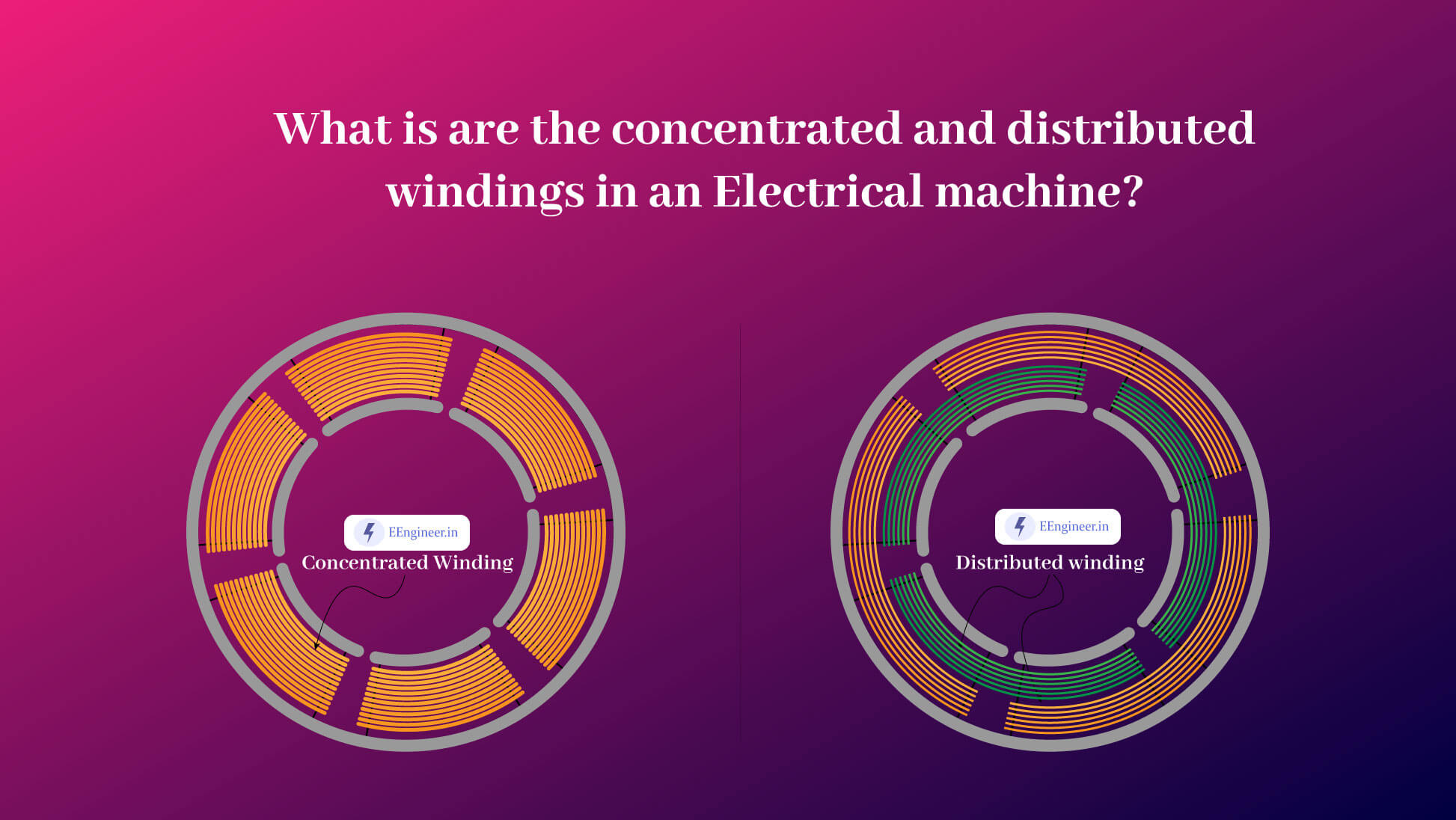
2. Slot Distribution
A distributed winding system, where the coils are spread across multiple stator slots, enhances the winding factor by reducing harmonic content and improving electromagnetic efficiency.
3. Winding Configuration
There are various winding configurations, such as lap winding, wave winding, and concentric winding, each impacting the winding factor differently. The optimal choice depends on the machine’s application and performance requirements.
Applications of Winding Factor Optimization
Different industries benefit from optimizing the winding factor in electrical machines. Some key applications include:
- Aerospace Industry – High-performance motors used in aircraft require efficient windings to reduce weight and increase reliability.
- Medical Equipment – Precision medical devices, such as MRI machines, rely on optimized winding designs for accurate electromagnetic field generation.
- Energy Storage Systems – Batteries and renewable energy systems use efficient winding techniques to improve energy conversion and reduce losses.
For advanced winding solutions and precision engineering, Winding Factor plays a crucial role in designing state-of-the-art electrical machines that cater to modern industrial needs.
Final Thoughts
The winding factor is a vital consideration in the design and performance of electrical machines. By understanding its impact and optimizing the winding layout, engineers can enhance efficiency, reduce losses, and improve overall machine performance. Whether in aerospace, medical, or energy applications, an optimized winding factor ensures superior functionality and reliability in electrical machines.